29th March 2018
The Mentalizing Loop is an important tool for devising and situating mentalization-based interventions in a structure within a session. It provides a framework for connecting the therapist’s observations of a family's or an individual's interaction patterns with underlying feeling states and related thoughts.
Furthermore, it helps clients or family members to experiment with new behaviours and actions.
The Mentalizing Loop is a framework, versions of which have been developed within individual and family (MBT-F) applications, which:
In sessions it is not always necessary or even desirable always to take each step one after the other, but for the less experienced therapist it may at the outset helpful to do so, whereas more experienced clinicians may at times wish to ‘skip’ steps. The purpose is to offer a basic structure for the therapist to follow when the content of a session, the rising an falling of different affective states, is moving quickly.
These steps are not a simple cycle, but are better conceived of as a SPIRAL; return to a "previous" step, is never quite the same, as this can only occur in the context of shared experiences and learning that were not present at the 'first pass'. So these are not merely linear steps which need to be taken in a prescribed order, but they are looped. Hence our attempt to represent the model as a spiral. It is possible to skip a few steps, or move across to another ‘step’, as well as going back to an earlier one.
At each or any step it is possible to use specific mentalizing techniques (see Mentalizing manoeuvres) which aim to generate specific mentalization processes in individuals or family members.
So whilst in order to explain the usefulness of the Mentalizing Loop, the model is presented here in a linear fashion, starting from how the therapist uses his process observation(s) of intra-family interactions and/or communication exchanges and how he feeds this back to the family, in an attempt to create reflexive process in each family member, the practice is much more fluid and allowing of the creative use of links.
Furthermore, it helps clients or family members to experiment with new behaviours and actions.
The Mentalizing Loop is a framework, versions of which have been developed within individual and family (MBT-F) applications, which:
- Allows therapists to structure sessions, or at least parts of sessions.
- Encourages mentalizing, providing a ‘route map’ which can be followed.
Not rigidly sequential
In sessions it is not always necessary or even desirable always to take each step one after the other, but for the less experienced therapist it may at the outset helpful to do so, whereas more experienced clinicians may at times wish to ‘skip’ steps. The purpose is to offer a basic structure for the therapist to follow when the content of a session, the rising an falling of different affective states, is moving quickly.

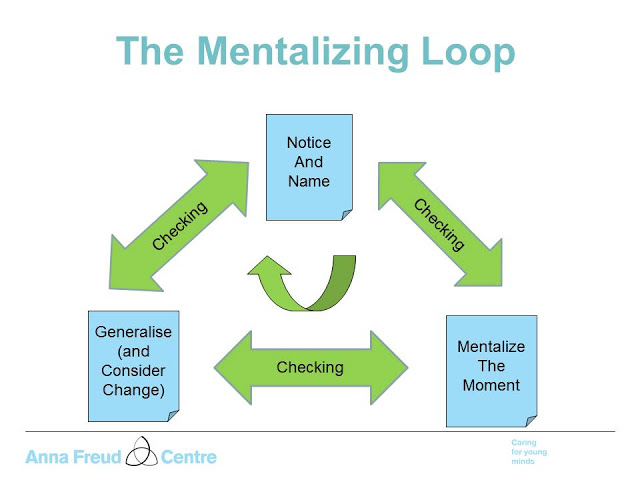
3 Steps and 3 Checks:
1. Notice and Name
Checking - "Is what I noticed, and the way it may link to what happens at home, what you guys see, too?"
2. Mentalize the Moment
Checking again - "So do we think we have got an accurate enough understanding of this pattern...?")
3. Generalize (and Consider Change)
Checking again - "So where are things now?"
Checking (in case you missed it)
Checking is in many ways at the very heart of mentalizing practice
A Spiral, not a Cycle
These steps are not a simple cycle, but are better conceived of as a SPIRAL; return to a "previous" step, is never quite the same, as this can only occur in the context of shared experiences and learning that were not present at the 'first pass'. So these are not merely linear steps which need to be taken in a prescribed order, but they are looped. Hence our attempt to represent the model as a spiral. It is possible to skip a few steps, or move across to another ‘step’, as well as going back to an earlier one.
At each or any step it is possible to use specific mentalizing techniques (see Mentalizing manoeuvres) which aim to generate specific mentalization processes in individuals or family members.
So whilst in order to explain the usefulness of the Mentalizing Loop, the model is presented here in a linear fashion, starting from how the therapist uses his process observation(s) of intra-family interactions and/or communication exchanges and how he feeds this back to the family, in an attempt to create reflexive process in each family member, the practice is much more fluid and allowing of the creative use of links.