31st December 2012
Why?
Some principles of Assessment for Drugs and Alcohol: Making a good assessment of a young person's drug and alcohol use is key because:- The assessment is an important INTERVENTION in and of itself - especially if it is properly handled.
- A good assessment helps to set the scene for the most appropriate Care Plan
- Young people using drugs and alcohl are at greater RISK than those who are not
What to do?
The UK's National Treatment Agency (NTA) has produced a good document that covers the essentials of assessing a young person's substance use in great detail. See NTA - Assessing Young People for Substance Use.
For guidance contained within this manual, see below.
1. DRUG/ALCOHOL HISTORY
Taking a good Substance Use History is important. (If you are using the ICR function in this manual, then you can use the form at Make or View Client Notes to record this.
2. ADDITIONAL KEY INFORMATION:
There are three key additional areas that should be enquired about in an assessment IN ADDITION to the drug and alcohol history:
(a) Risks: You can use the RiskAssessment at Make or View Client Notes.
(b) Mental Health, other Comorbidities, and Resiliences: You can use the AIM and consultation with the team/Psychiatrist via SupervisoryStructures. Remember there are Multiple interacting aetiologies for adolescent Substance Use Disorder, and within resiliencies you will be looking at Family and other pro-social relationships within the young person's social ecology.
(c) Stage of Change: You can refer to Assess Stage of Change, and record this under the Formulation and Treatment Aims via Make or View Client Notes. This is key to fulfilling one of the key SUD-Rx principles, which is that, as practitioners you should Adapt your Discourse to fit where the young person is re. the Stages of Change.
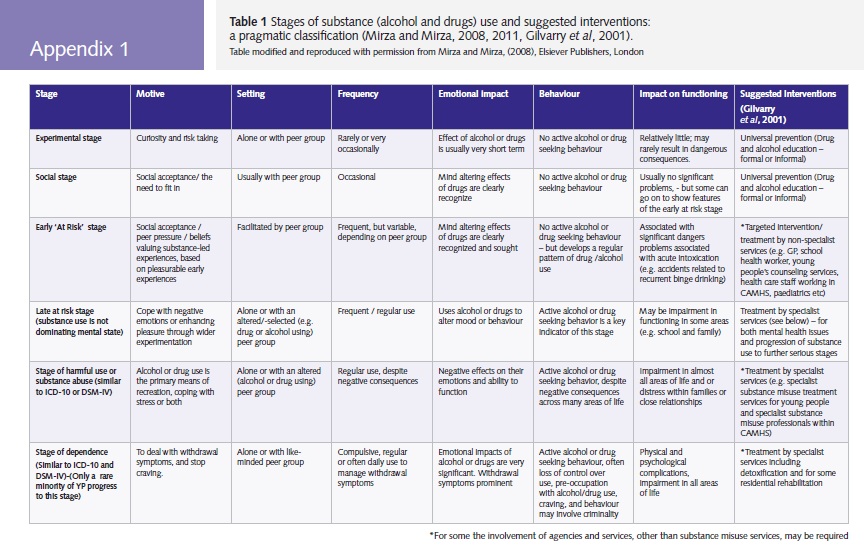
It is helpful to clarify what STAGE the young person is at: the following grid adapted from Mirza and Mirza (2008) Adolescent Substance Use offers helpful markers along the route to harmful and dependent use in youth, that are more relevant to the Developmental Considerations that "set the scene" in which this drama unfolds.
(There is a direct external link to this table here) and SEE BELOW FOR THE ALL-IMPORTANT FEEDING BACK of your findings to the young person:
3. ASSESSMENT = INTERVENTION! - Giving FEEDBACK
You must GIVE FEEDBACK. Giving clear, personalised feedback about the assessment is a key part of the assessment; where an Assessment actually becomes an Intervention. See Assessment for SUD-Rx - Giving Feedback.